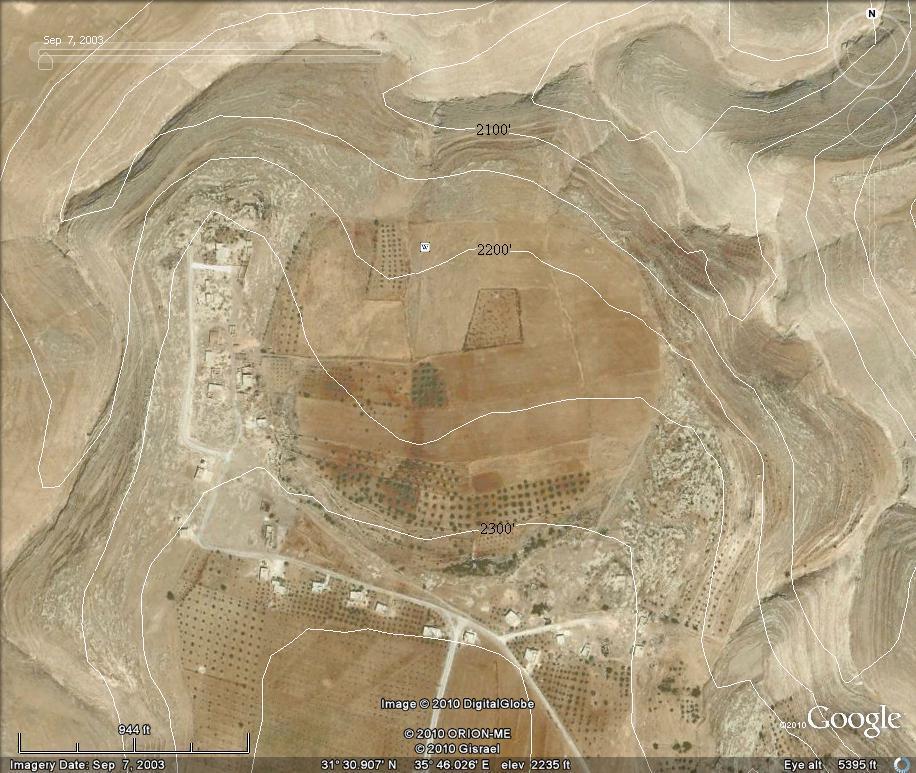

Large circular ground feature at Adh Dhuhaybah, Amman Governorate, Jordan
Alternate names: Edh Dhuheiba - El Deheibe
Geographical coordinates: 31 deg 30 min 55 sec N, 35 deg 46 min 02 sec E.
The interior circular area, under cultivation and with orchards, is about 530 meters in diameter. The total diameter (where the rocky exterior ring rises above the surrounding terrain) is about 750 meters. I attribute the missing northeastern portion of the rocky ring to be due to erosion. Overall, the ground slopes downward to the Northeast.
This structure is located 1.1 miles (1.8 Km) Northwest of the ancient Moabite city of Dibon. The present day town of Adh Dhuhaybah has been built on the western and southern portion of the rocky surround.
There are mineralogical tests that are required to establish whether or not a feature is caused by meteor or asteroid impact. Until these are done, my tentative identification of this ringed structure as a meteorite impact crater must remain as a speculation.
23 October 2010
To review the study that lead to finding this circular feature, please visit:
The Other Herodium.
[Added 24 Oct 2010.]
Here is a Google Earth bird's-eye-view of the candidate impact structure. Elevation contours were drawn in using Google Earth's "path" function. The ancient Dibon mound and the modern day Dhiban can be seen in the upper left of the image.
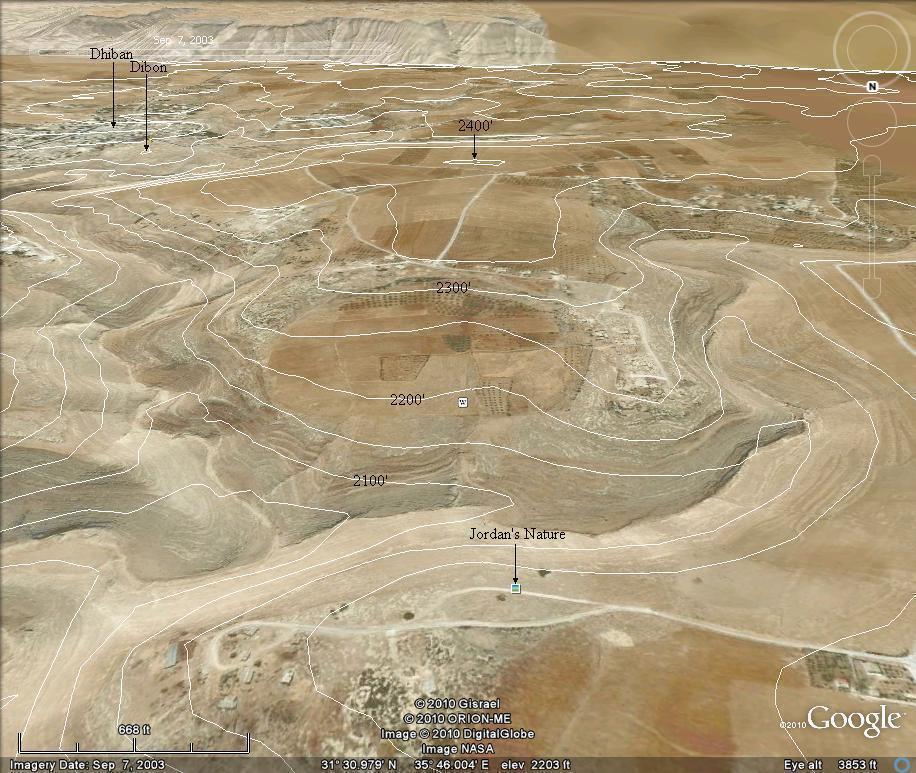

Adh Dhuhaybah atop it's circular foundation as seen from the North
[Added 31 Oct 2010. Replaced with cloud-free image on 01 Jan 2011.]
Update Added on 30 Dec 2010
I originally speculated that the limestone rocky area encircling about half of the structure may have been a crater-rim where long time weathering has caused the sharp edge of its rim to be removed.
The Mesha Stele (A.K.A. The Moabite Stone), erected in ancient Dibon one mile from the circular feature, is made of blue-black basalt. I'd like to find out the degree of mineralogical similarity (or dis-similarity) between any basalt rocks found in the area and the material of the Moabite Stone.(1)
In August 2017 there was a Jordan's Nature Panoramio photograph (number 5736613) which showed what might be a lone grey basalt rock lying on the ground, seen in the lower right hand corner of the picture. The camera location for this photo was apparently 0.32 mile (515 meters) NNW of the center of the circular structure. A Jordan's Nature icon on Google Earth, used to take you to this photo, but Panoramio has been discontinued. [Updated on 06 Oct 2018.]
Electrical Discharge Speculation - 08 Mar 2017

Interior of Adh Dhuhaybah Feature, viewed from the North
If the so-called "crater" turns out not to have been caused by a meteorite impact, then I suggest that the feature was a point of contact for an interplanetary (or earth-moon) electrical discharge, as theorized by Immanuel Velikovsky(2).
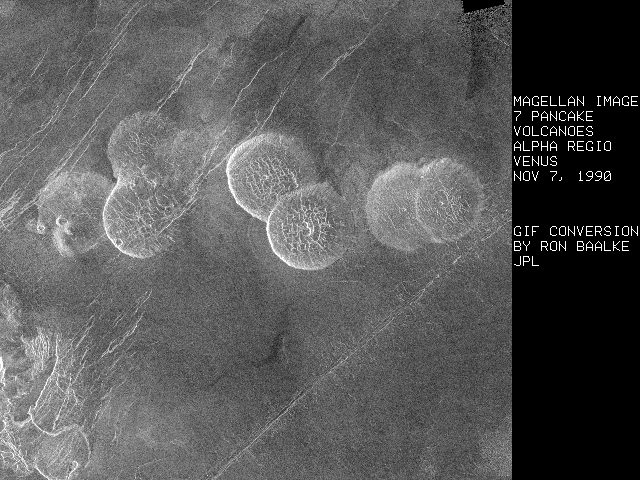
Here is a Magellan RADAR image of the surface of Venus which shows a string of what some researchers call "pancake volcanoes." (Pro-Velikovsky) Electric Universe researchers offer the idea that these structures look just like Lichtenberg electrical discharge patterns.(3)
References
(1) T.G. Bonney, The Basalt of the Moabite Stone, The Geological Magazine, New Series, DECADE IV. VOL. IX. January - December,
(1902), pp. 493-495
(2) Immanuel Velikovsky, Worlds in Collision, Macmillan Company (1950), pp. 272-273.
(3)